Mumbai: Dr. Shivraj Ingole, Professor and Interventional Radiologist, JJ Hospital and Grant Medical College, Mumbai, says that Deep Vein Thrombosis is a condition in which a blood clot forms inside a vein somewhere in the body. Deep vein thrombosis mostly occurs in the lower leg or thigh, although it can sometimes occur in other parts of the body as well. A blood clot is clotted blood that can move with the blood to other places. This comes across as a complication of the operative procedure. In most cases, it is not recognized until a person has to go to emergency services to be diagnosed with a pulmonary embolism. This means that a blood clot has traveled through the leg to the lungs and is causing a blockage in an important artery. When a clot forms, it can spread to areas around the vein, causing a localized swelling that can encourage the development of additional blood clots.
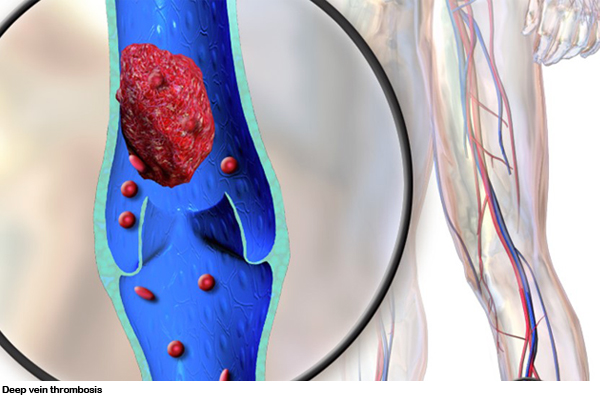
What are the symptoms of DVT? On this question, Dr. Ingole says that there is swelling of the leg, weakness of the muscles of the leg or arm, red or discolored skin on the leg, feeling of heat in the affected leg, swelling of the arm or hand, blue spot from the arm. Wrist pain, sudden shortness of breath, chest pain or discomfort that gets worse when you take a deep breath or cough, feel dizzy or dizzy, or faint. Its main symptoms are rapid pulse, bloody cough etc.
What causes DVT? On being asked, Ingole says that blood clots can be formed due to injury in any pulse. Too much rest and lack of movement increases the risk of DVT. Sedentary lifestyle/inactivity leads to accumulation of blood in the legs. Gradually it develops into a clot. Certain medications can increase the chances of blood clots forming. Weight gain also increases the risk of DVT. Birth control pills or hormone therapy, excessive smoking, sedentary life, blood clotting disorders, cancer, abdominal pain increase the risk of DVT.
How is DVT diagnosed? In response the doctor says that the most common test to diagnose deep vein blood clots is color duplex ultrasound. It is a painless, quick and non-invasive test. it is the best. Sometimes MR venography is needed to know the extent of the disease and May-Thurner syndrome. May-Thurner syndrome is a clinical entity of left iliac vein compression by the right iliac artery, resulting in isolated left lower extremity swelling and may be a precipitating factor for ileofemoral deep venous thrombosis. Magnetic resonance imaging is the best method for diagnosing this entity as it can rule out the presence of pelvic mass and deep venous thrombosis, demonstrating the anatomy characteristic of this syndrome.
What are the treatment options for Deep Vein Thrombosis? On asking Ingole says that Deep vein thrombosis is usually treated with anticoagulants, also known as blood thinners.
Ileofemoral or large vein stents have shown good long-term clinical outcomes in both chronic thrombotic and non-thrombotic deep venous disease. Patients with ileofemoral DVT are at particularly high risk for post-thrombotic syndrome and late-stage disability. CDT has significant potential to prevent post thrombotic syndrome and offers distinct advantages compared to surgical venous thrombectomy, systemic thrombolysis, and anticoagulation alone.
Adjunctive CDT is likely to provide faster symptomatic relief than anticoagulation alone and does not increase the risk of symptomatic PE.
What is Post Thrombotic Syndrome (PTS)? Doctors say that PTS is a chronic condition that is defined as a group of symptoms and signs that develop months to years after an acute DVT. These include daily limb aches and/or pain, fatigue, heaviness, and/or swelling that get worse with direct position and activity. In severely affected patients, venous stiffness, stasis dermatitis, subcutaneous constriction, fibrosis, and/or skin ulceration may develop.
What is Pharmaco Mechanical Catheter Guided Therapy (PCDT)? In response, the doctor says that pharmacomechanical catheter directed thrombolysis (PCDT) involves the combined use of catheter directed thrombolysis and catheter-based suction or mechanical thrombectomy.
Thrombolysis is a minimally invasive procedure in which we inject clot-dissolving drugs directly into the clot to break it up. in the process of treatment
Eat light food at night, then do not eat or drink anything after midnight. We will provide you with more detailed information about what medicines you can take before and in the morning of the procedure. Plan to have someone take you home after the procedure.
